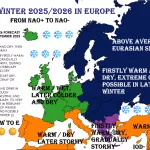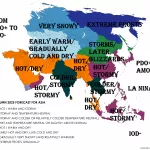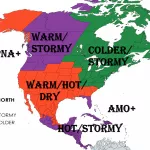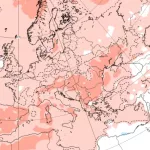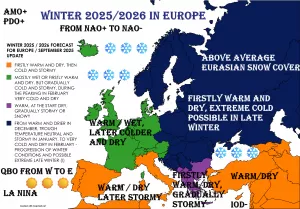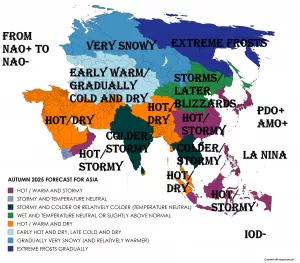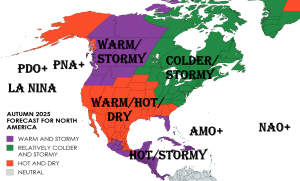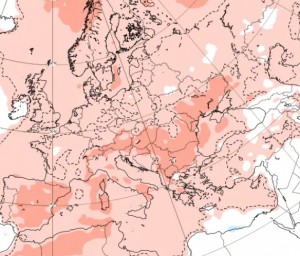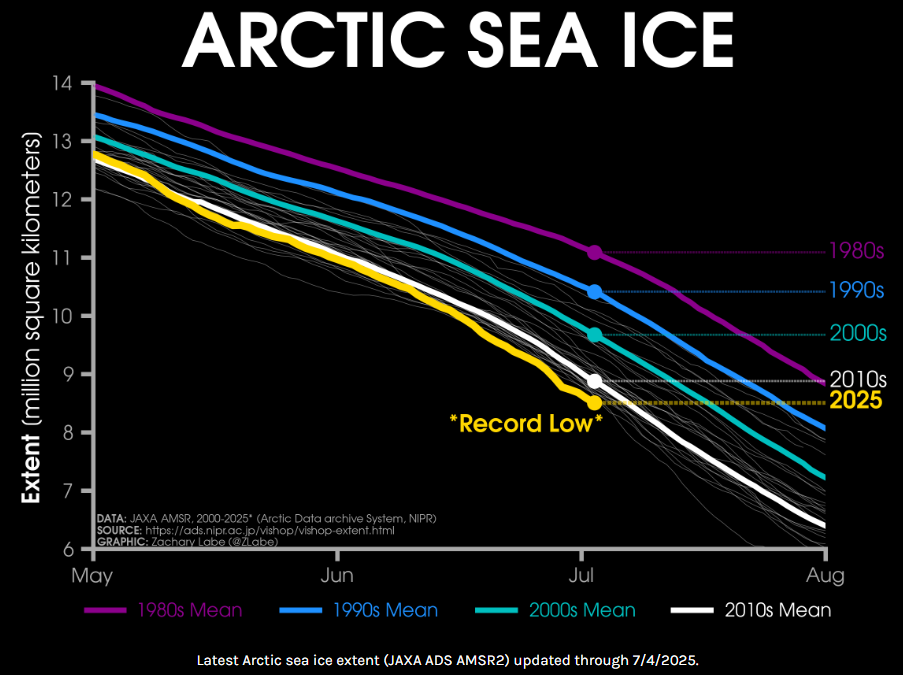
Arctic sea ice has plunged to its lowest extent on record for early July 2025, according to data from Zack Labe. Satellite observations (JAXA & NSIDC) show a dramatic drop below previous years, setting new benchmarks in the 45-year satellite era.
After June 2025 ended as the 2nd lowest June on record, early July has pushed even further, with rapid melting weeks ahead of schedule. Current ice extent is over 1.2 million km² below the 1981–2010 average.
This steep decline matters: less sea ice means more solar absorption, accelerating warming through the ice–albedo feedback loop. It also raises the risk of an all-time low September minimum, potentially beating the 2012 record.
Impacts go beyond the Arctic—melting sea ice disrupts weather patterns globally, fuels ocean warming, and harms polar ecosystems. The early-July record confirms long-term trends and hints at a future with ice-free Arctic summers in the coming decades.
In short:
🔴 Lowest Arctic sea ice extent ever measured in early July
🧊 September record in sight
🌍 Climate signal, not a fluke
Outlook: Arctic Sea Ice – July to September 2025
The outlook for the rest of the 2025 melt season is increasingly concerning. Based on current conditions and model projections, here’s what to expect:
Continued Rapid Melting Likely
- The Arctic is entering its peak melt period (mid-July to early August).
- Warm air intrusions, low cloud cover, and increased ocean heat are expected to persist, especially in the Laptev Sea, East Siberian Sea, and Beaufort Sea.
- Ice in these regions is already thin and fragmented, making it vulnerable to complete loss by August.
Potential for Near-Record or Record-Low September Minimum
- If melting continues at the current rate, September 2025 could approach or surpass the all-time low from 2012 (~3.39 million km²).
- Even a “normal” melt rate from now through August would likely place 2025 in the bottom 3–5 years of all time.
Feedback Loops Amplifying the Melt
- Ice–albedo feedback (dark ocean absorbs more heat) is now in full swing.
- Warm Arctic waters from earlier spring anomalies are maintaining high sea surface temperatures.
- Atmospheric circulation (jet stream patterns) may continue to funnel warm air into Arctic regions.
Ecological and Climatic Consequences
- Wildlife like polar bears, walruses, and Arctic seabirds will face habitat disruptions.
- Permafrost regions along the Arctic coast may see increased thawing and methane release.
- Changes in sea ice extent can disrupt jet stream behavior, influencing weather extremes in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Bottom Line:
The outlook is poor for Arctic sea ice through summer 2025. All indicators point toward:
- One of the lowest sea ice extents on record
- Greater climate feedbacks
- A strong warning that the Arctic is approaching a tipping point

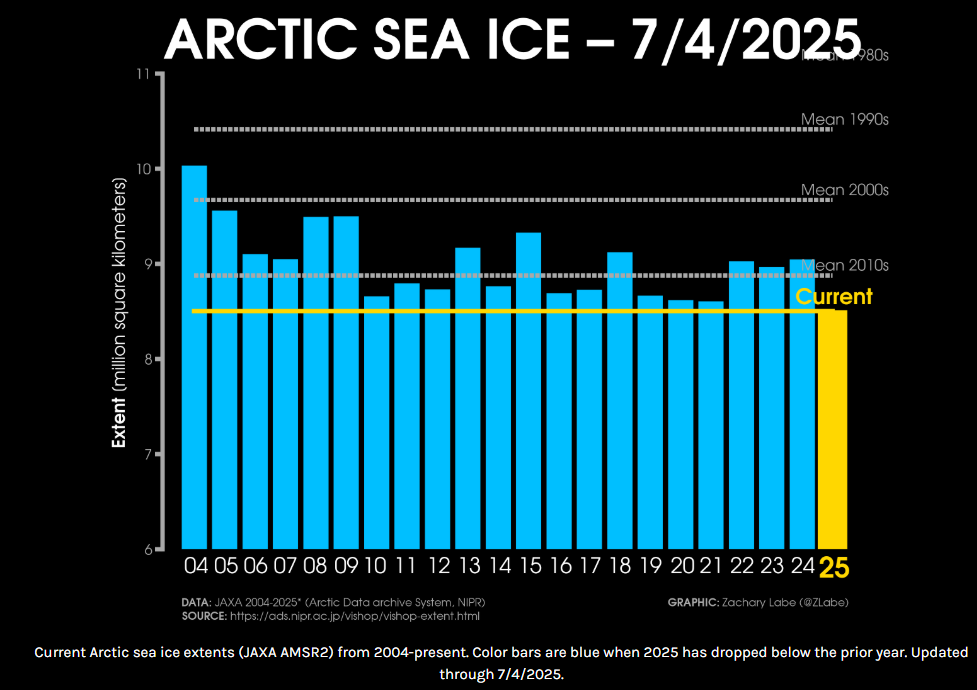
Source: https://zacklabe.com/arctic-sea-ice-extentconcentration/