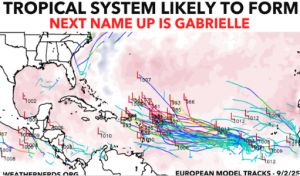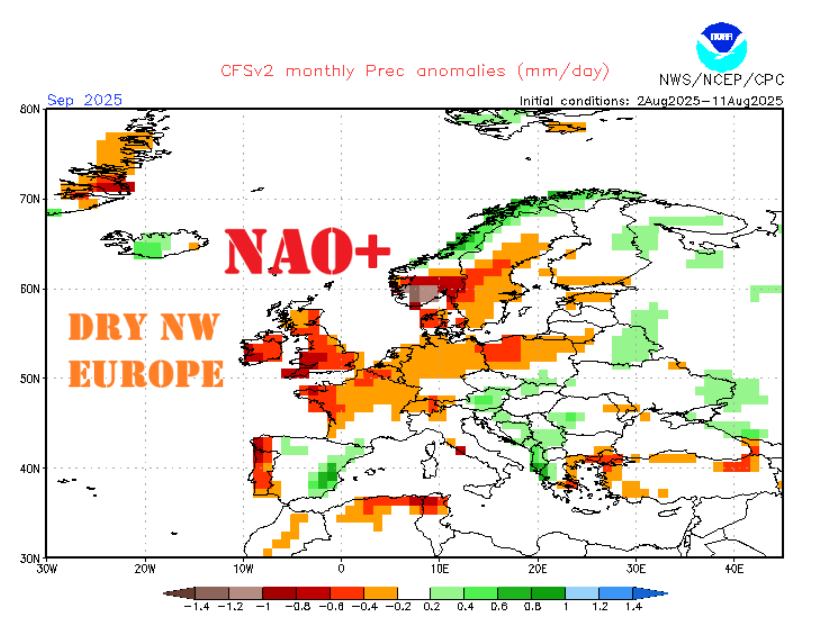
Climate models indicate a likely positive North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO+) phase for September 2025, based on data derived from the Climate Forecast System (CFS) and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) teleconnection graphs. The NAO is a critical atmospheric pattern influencing weather across the North Atlantic region, including Europe, Greenland, and parts of North America.
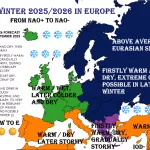
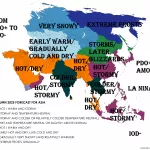
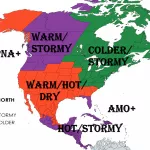
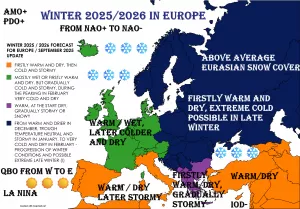
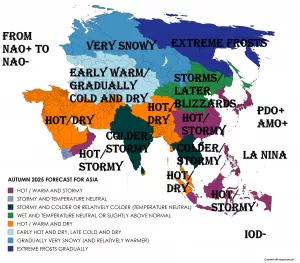
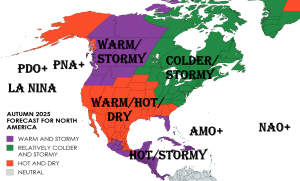
A positive NAO phase typically features a strengthened pressure gradient between the Icelandic low and the Azores high, resulting in enhanced westerly winds across the North Atlantic. This pattern tends to bring milder and wetter conditions to Northernmost Europe and drier, warmer weather to NW Europe, Southern Europe and the Mediterranean during the transition from summer to autumn.
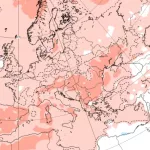
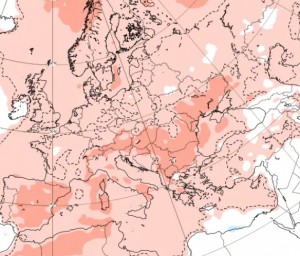
The CFS forecast map for September 2025 shows elevated pressure anomalies over the Azores and a deepened low-pressure system near Iceland, consistent with a NAO+ setup. Similarly, ECMWF teleconnection graphs support this forecast, highlighting increased positive indices throughout the month.
The implications of a NAO+ in September include potential for:
- Above-average rainfall and mild temperatures in northernmost Europe, possibly leading to early autumn storms and wetter conditions.
- Dryer and warmer weather in NW Europe, southern Europe and the Mediterranean basin, increasing the risk for drought stress in vulnerable regions.
- Potential impacts on agriculture, energy demand, and water resource management across affected zones.
Understanding the NAO phase is vital for medium-term seasonal forecasting and planning, as it strongly modulates temperature and precipitation patterns. If confirmed, the September 2025 NAO+ could influence the early autumn weather regime significantly, warranting attention from meteorologists, policymakers, and stakeholders across Europe and adjacent regions.

Source of CFS forecast: https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/CFSv2/imagesInd3/euPrecMonInd1.gif
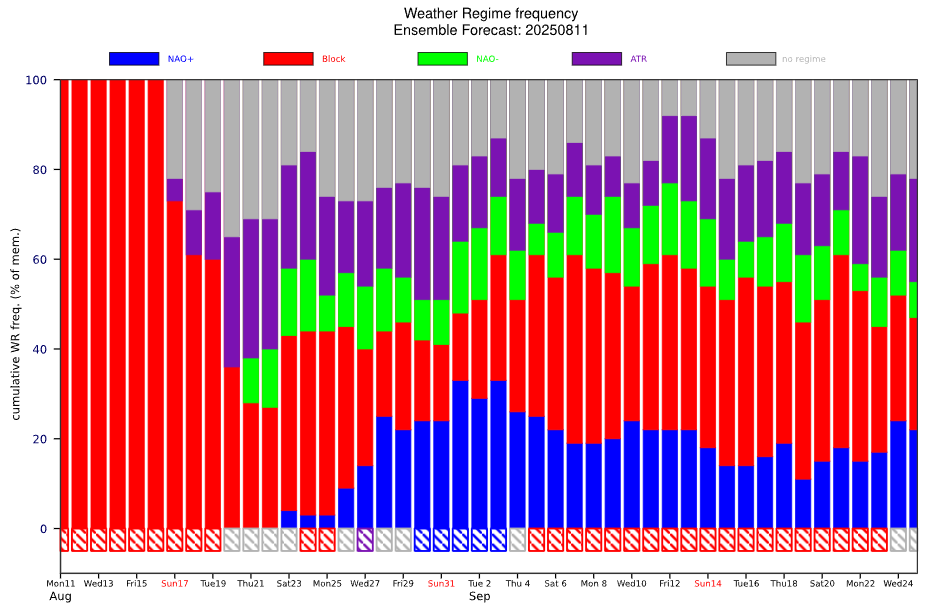
ECMWF Outlook: https://charts.ecmwf.int/products/extended-regime-probabilities?forecast_from=latest