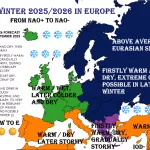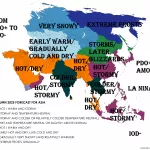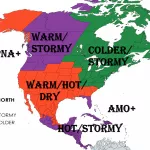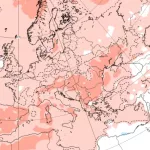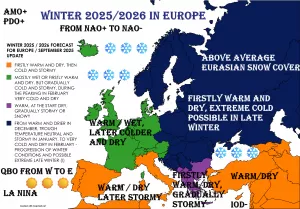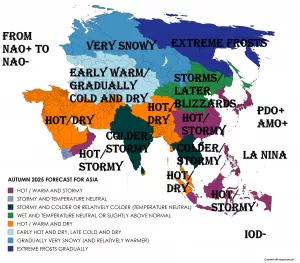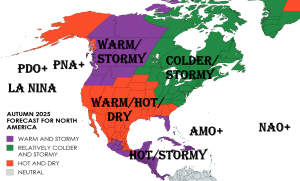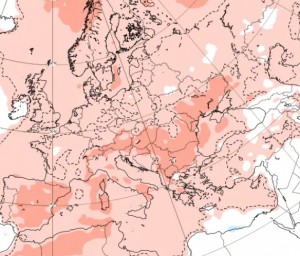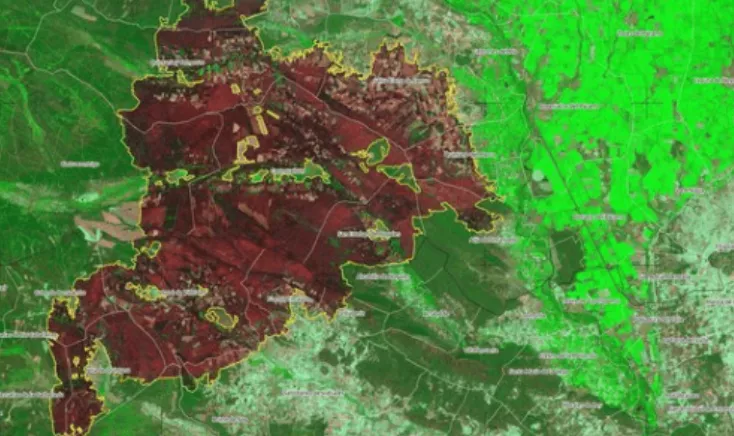
Spain is facing its largest recorded wildfire in history, raging across Molezuelas in Zamora. The massive blaze has already claimed three lives, leaving communities devastated and prompting emergency responses at national and regional levels.
Extent and Intensity
The wildfire in Molezuelas has spread rapidly across dry forests, scrubland, and farmland, fueled by extreme heat and prolonged drought. Meteorologists point to the historic Iberian heatwave of August 2025 as a key factor, with record temperatures in northern and central Spain (e.g., Cantabria +43.5°C, Asturias +42.9°C, Barcelona +38.9°C) creating ideal conditions for wildfire ignition and propagation.
- Location: Molezuelas, Zamora, Castile and León
- Casualties: 3 confirmed dead
- Area burned: Thousands of hectares, ongoing containment efforts
- Wind influence: Moderate northerly winds spreading flames rapidly across valleys and ridges
Meteorological and Environmental Factors
The extreme fire behavior has been driven by a combination of environmental conditions:
- Historic heatwave: Days of +40°C and above, record-breaking temperatures in surrounding regions.
- Prolonged drought: Vegetation extremely dry, creating a highly combustible environment.
- Low humidity: Relative humidity below 20% for consecutive days, facilitating rapid flame spread.
- Topography: Valleys and ridges channel winds, allowing fire fronts to move at alarming speed.
Impacts on Communities
The wildfire has devastated local communities, forcing evacuations and causing property losses:
- Villages in Zamora province were evacuated as flames approached residential areas.
- Emergency services deployed hundreds of firefighters, helicopters, and ground support to contain the blaze.
- Infrastructure, including roads and power lines, has been damaged, disrupting daily life.
- Agricultural lands have suffered total losses, affecting crops, pastures, and livestock.
National Significance
This event has been described as the largest wildfire in Spain’s recorded history, highlighting the vulnerability of the country to extreme climate events. Analysts note that climate change, prolonged drought, and record-breaking heatwaves are contributing to increasingly catastrophic fire seasons across Spain and the Mediterranean region.
Response and Outlook
Authorities continue firefighting operations, though containment is challenging due to the size of the blaze and ongoing high temperatures. National and regional governments have issued warnings for other provinces, emphasizing vigilance and emergency preparedness.
Experts warn that until temperatures normalize and rainfall returns, Spain may continue to face exceptionally high wildfire risk, particularly in central and northern regions affected by extreme heat.

Illustration map. Source: Yolanda Clemente X