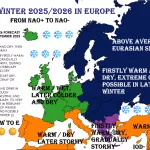
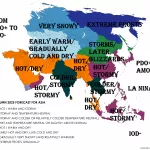
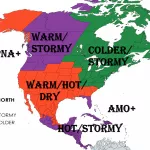
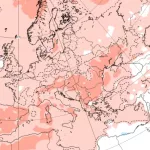
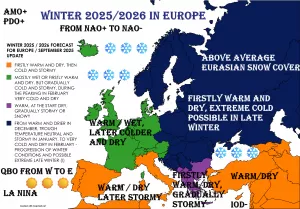
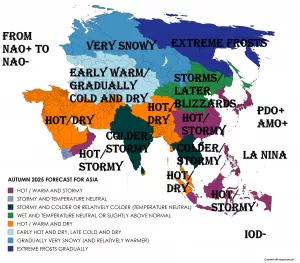
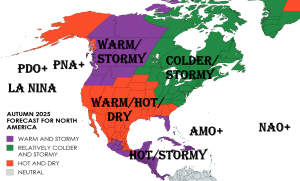
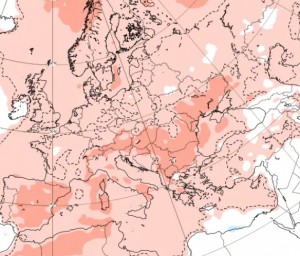
Vize Island, located at 79°N in the Arctic Ocean, has experienced a record-breaking warmth streak, with no recorded sub-zero temperatures for minimally 35 consecutive days in late summer 2025. Normally, late August and early September see nightly temperatures dropping below 0 °C, but this extended period of warmth is highly anomalous for such high latitudes.
Meteorological Factors:
- Persistent High-Pressure System: A stationary Arctic high-pressure ridge has maintained subsiding warm air, clear skies, and low wind speeds.
- Warm Air Advection: Southwesterly flows have transported warmer maritime air into the high Arctic, elevating near-surface temperatures.
- Sea Ice Retreat: Reduced sea-ice extent in the surrounding Arctic Ocean limits the usual cooling effect of melting ice, contributing to sustained warmth.
- Extended Daylight: Although solar angles are declining in late summer, long daylight hours at 79°N still contribute to surface heating.
Impacts and Significance:
- Permafrost Thaw: Prolonged above-freezing temperatures accelerate active layer deepening and permafrost degradation, which threatens infrastructure like weather stations, research buildings, and transport routes.
- Ecosystem Stress: Arctic flora and fauna adapted to regular freeze-thaw cycles may experience disruption in growth, breeding, and foraging.
- Glaciology & Sea Ice: The lack of freezing contributes to reduced sea ice formation, affecting local albedo and increasing Arctic warming feedback loops.
- Scientific Monitoring: This event provides critical data on Arctic amplification and extreme warming trends, as consecutive non-freezing days at 79°N are extremely rare historically.
This 35-day streak above freezing underscores the intensification of Arctic warming trends, showing that high-latitude regions are experiencing increasingly prolonged warm periods, which have cascading effects on permafrost, sea ice, and polar ecosystems.
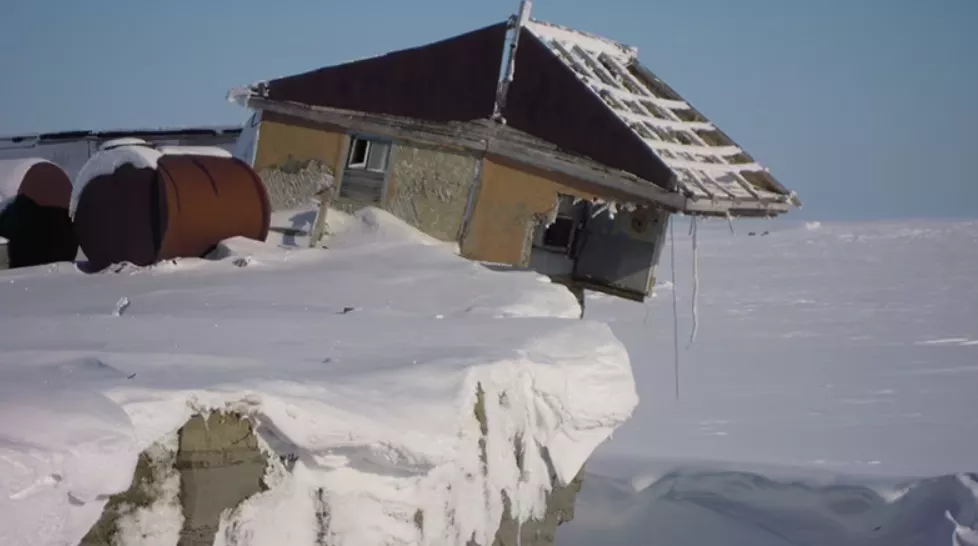
Vize Island´s Weather Station was shifted due to Melting Permafrost!
The Vize Island Weather Station, located at 79°N in the high Arctic, has been relocated in 2025 due to structural instability caused by melting permafrost. The station, a critical node for long-term Arctic climate monitoring, experienced ground subsidence and foundation instability, which threatened both instrument accuracy and operational safety.
Permafrost Melting Context:
- Permafrost degradation in the Arctic has accelerated in recent decades, with rising air temperatures and prolonged warm periods causing the active layer (seasonally thawed surface soil) to deepen.
- Subsidence and deformation occur when ice-rich permafrost thaws, leading to uneven settling of structures and potential damage to meteorological instruments.
- The Vize Island station is located on low-lying terrain, which is particularly susceptible to thaw settlement.
Relocation Measures:
- The station has been moved to a more stable area with higher elevation and better drainage to reduce thawing impact.
- Foundation improvements include elevated platforms and adjustable supports to compensate for ongoing permafrost variability.
- Instruments have been recalibrated to ensure continuity and accuracy of temperature, wind, humidity, and precipitation records.
Scientific and Operational Implications:
- The relocation highlights the practical challenges of Arctic meteorology under warming conditions.
- Long-term climate monitoring must now account for site changes when analyzing temperature and precipitation trends.
- This event underscores the vulnerability of Arctic infrastructure to climate change and the need for adaptive engineering solutions.
- Despite the move, the station continues to provide critical data on Arctic warming, sea ice variability, and permafrost dynamics, which are essential for global climate models.
Significance:
The Vize Island Weather Station relocation serves as a tangible example of climate change impacts on human-built infrastructure in the Arctic. It illustrates that even well-established research sites must adapt to permafrost melt, ensuring continued high-quality scientific observations in one of the most climatically sensitive regions of the planet

Vize island weather station shifted due to melting permafrost. Source: https://www.climatechangenews.com/2016/08/11/in-pictures-russian-weather-station-on-the-edge-of-melting-permafrost/