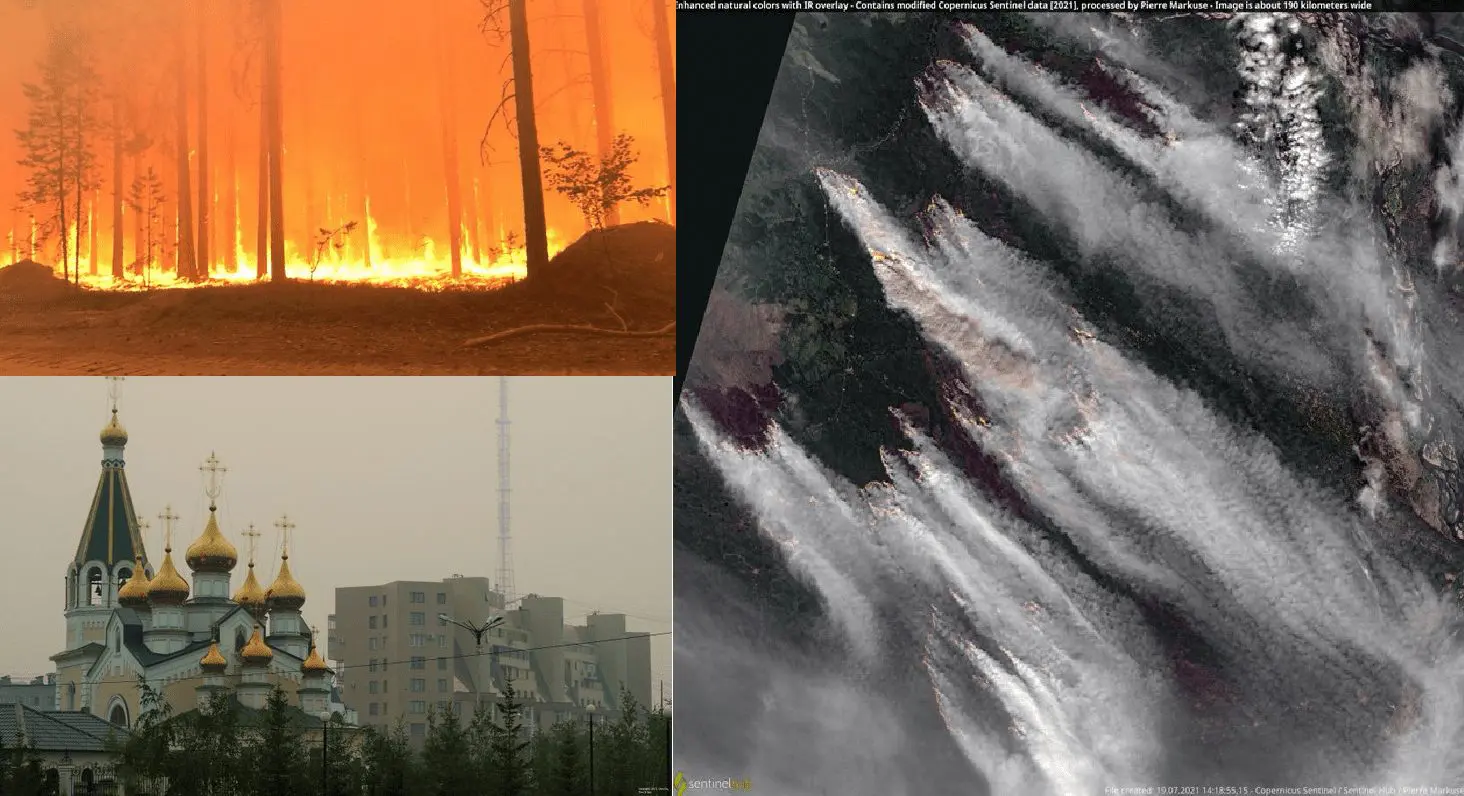
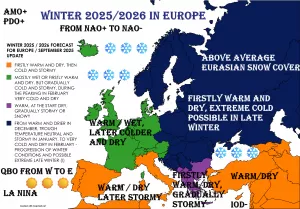
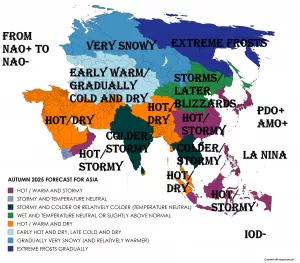
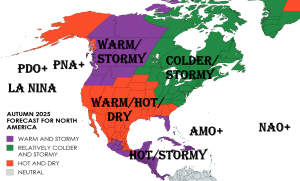
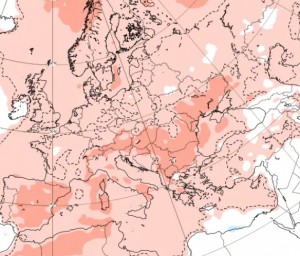
Russia’s coldest region (Yakutsk region) lost 2,5 million hectares of forests in the 2021 season’s fires.
After June 2021 heatwaves, when the temperature in Jakutsk reached super tropical +35,4°C (a new all-time June record for the city) and only 1 day between 18. June and 5. July 2021 wasn´t tropical (maximum temperature above +30,0°C), the next heatwave appeared in the region in the last days, with measured +32,5°C in the city on Monday, 19. July 2021.
Short, but intense heatwave leads to the strengthening of wildfires across all Eastern Siberia – in the Yakutsk region (Sakha) is currently choking around 100 cities and settlements, including the capital city, Yakutsk, where the airport was closed and toxic air is threatening sensitive groups of the population.
Some desperate communities have reportedly even drafted children into the fight to hold back the flames, according to watchers on Twitter.
Military planes have been used to seed clouds with silver iodide and liquid nitrogen to induce rainfall.
Russia is using climate engineering to trigger rainfall!
Emergency workers have been using climate engineering technology to combat the inferno – silver iodide cartridges were delivered directly into the clouds from Antonov An-26 transport planes.
The Convention on the Prohibition of Military or Any Other Hostile Use of Environmental Modification Techniques (ENMOD) is the only international framework related to the regulation of weather and climate modification technologies.
There are well-known cases of affecting weather in China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Israel, Kuwait, United Arab Emirates, Southeastern Asia (Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam War…), Sri Lanka, USA, Canada, Bulgaria, France, Spain, Russia, Germany, Slovenia, the UK, Australia, Mali, and Niger.
In mid-altitude clouds, the main know-how is associated with the fact that the equilibrium vapor pressure is lower over ice than over water. The formation of ice particles in supercooled clouds allows those particles to grow at the expense of liquid droplets. The particles become heavy enough to fall as precipitation from clouds /=static seeding/.
Seeding of warm-season or tropical cumulonimbus (convective) clouds seeks to exploit the latent heat released by freezing. The additional latent heat adds buoyancy, strengthens updrafts, ensures more low-level convergence, and ultimately causes rapid growth of properly selected clouds. /=dynamic seeding/.
In February 2009, China used iodide over Beijing to artificially induce snowfall after 4 months of drought. The snowfall in Beijing lasted for approximately three days and led to snow calamity and the closure of 12 main roads in the Beijing region.
If technology is used not reasonably, effects such as heavy rainfall, hailstorms, or snow calamities are possible.
Near fight with wildfires, it appears, that artificial intervention into nature should have more positive than negative consequences, although it should affect changes in local or regional circulation regimes.