Only before a few days, we were informed about abnormally cold conditions in the Vostok station region, Antarctica (30. September 2021, -79,4°C measured – what is only 0,6°C below all-time October world record /https://mkweather.com/vostok-794c-only-06c-from-the-all-time-october-record/; https://mkweather.com/antarctica-very-close-to-temperature-records-vostok-757c-dome-fuji-740c// and now, we are returning to Antarctica with another extreme record.
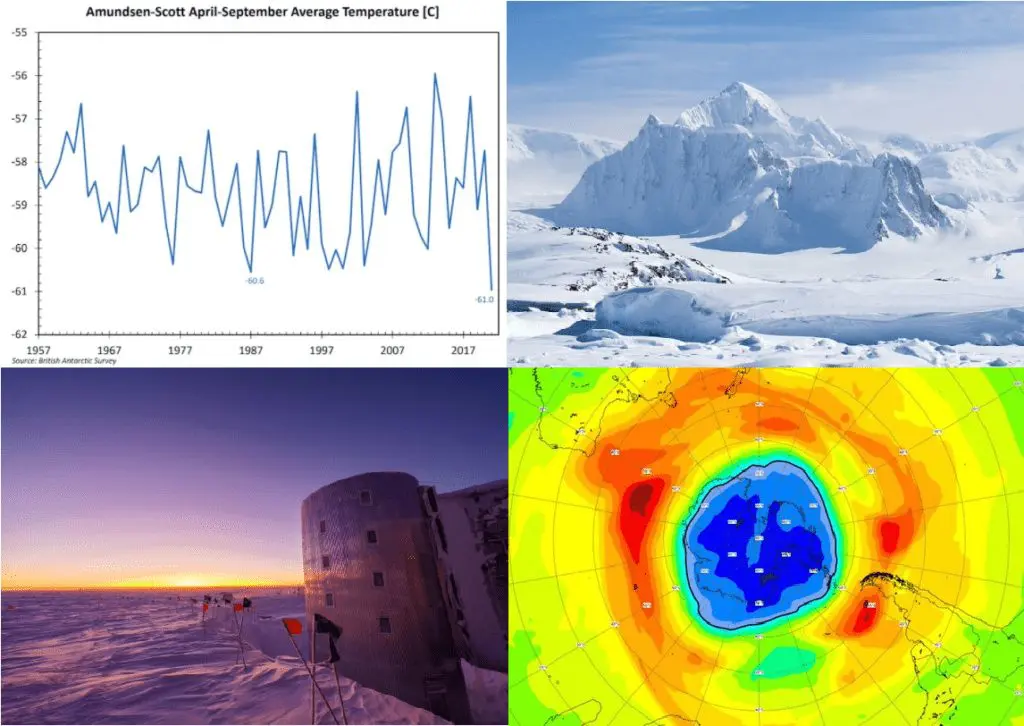
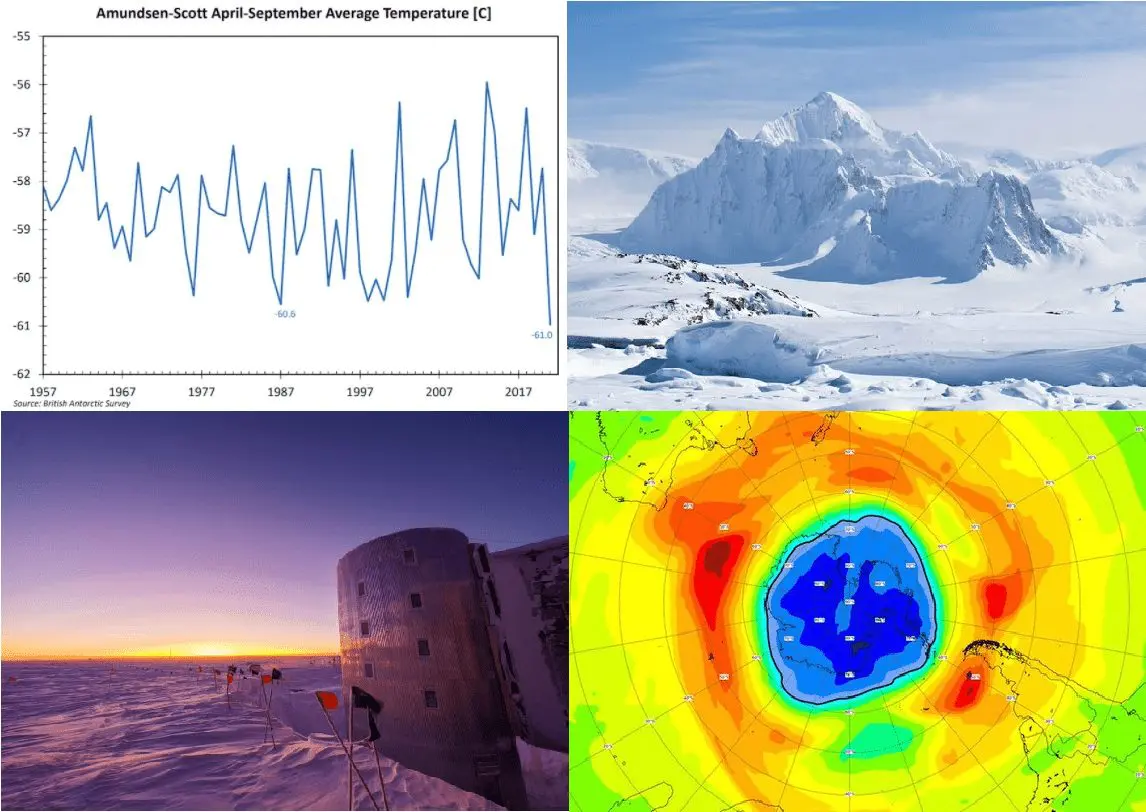
In the Amundsen Scott – South Pole weather station, the average temperature of Winter season 2021 (April 2021 – September 2021) reached only -61,0°C / -78°F, which is the coldest value in all-time history!
This was 2,5°C /4.5°F degrees lower than the most recent 30-year average at this remote station.
Similar was only a year 1987, with an average winter-season temperature of -60,6°C.
Such we mentioned in the previous article, extremely cold conditions in Antarctica are a work of climate change, mainly a positive phase of Antarctic Oscillation / positive phase of Southern Annular Oscillation (AAO+, SAM+).
Whether the southern polar vortex is strong or weak depends on cycles linked with AAO and SAM.
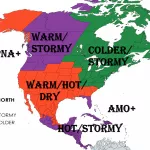
This phenomenon is associated with the ozone layer above Antarctica, but too with a changing climate in the region – some parts of the continent (mainly East Antarctica) are showing a cooling 40-years trend, thanks to the re-freezing Southern Ocean. /https://mkweather.com/east-antarctica-not-warming-past-4-decadescooling-trend/; https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/06/210623141711.htm/
Sweet water from the Antarctic glacier freezes around the continent, with a result of increasing albedo of the region and subsequent cooling tendencies.
On the contrary, surprisingly extreme coldwaves above the continents of the Southern Hemisphere (South America, South Africa, Australia, and Oceania) are associated mainly with opposite, AAO- / SAM- (negative phase of AAO / SAM), when the polar vortex is more destabilized and Antarctic fronts and cyclones hit southern parts of the continent more frequently.
According to Washington Post, “the strong polar vortex not only makes it very cold over Antarctica but accelerates processes that lead to stratospheric ozone depletion, which in turn can strengthen the vortex even more. This year’s ozone hole over Antarctica is much bigger than average at around 24 million square kilometers”.
Meanwhile in the Arctic, Arctic Sea Ice Extent yearly minimum (on 16. September 2021 at 4,72 million square kilometers (1.82 million square miles)) was 26% greater such as in the year 2020, 12-th lowest on record, and the greatest since 2014 /https://mkweather.com/arctic-sea-ice-extent-26-greater-than-last-year-12th-lowest-on-record-and-the-largest-since-2014//. Colder conditions around the world is bringing mainly La Nina pattern, which is forecasted to persist approximately until Autumn 2022 /https://mkweather.com/2022-2023-forecast-chances-for-el-nino//.
AAO+ phases are after the year 2000 much more frequent such as AAO-, with increasing trend, which means, that coldwaves in the next decades in Antarctica should be even stronger and for some species possible fights for survival.
Antarctica is therefore during climate change behaving totally oppositely such as the rest of the world (excluding Global Warming Holes) – expeditions across the continent will have to prepare to changed conditions, too.