After Mkweather Summer 2021 forecasts for Europe /https://mkweather.com/summer-2021-forecast-for-europe-hot-and-dry-pattern-as-leading-heatwaves-drought//, North America /https://mkweather.com/summer-2021-forecast-for-north-america-hot-stormy-east-and-dry-west// and Asia /https://mkweather.com/summer-forecast-for-asia-hot-but-strong-indian-monsoon//, we should look at outputs of forecast models for Winter 2021 in Australia.
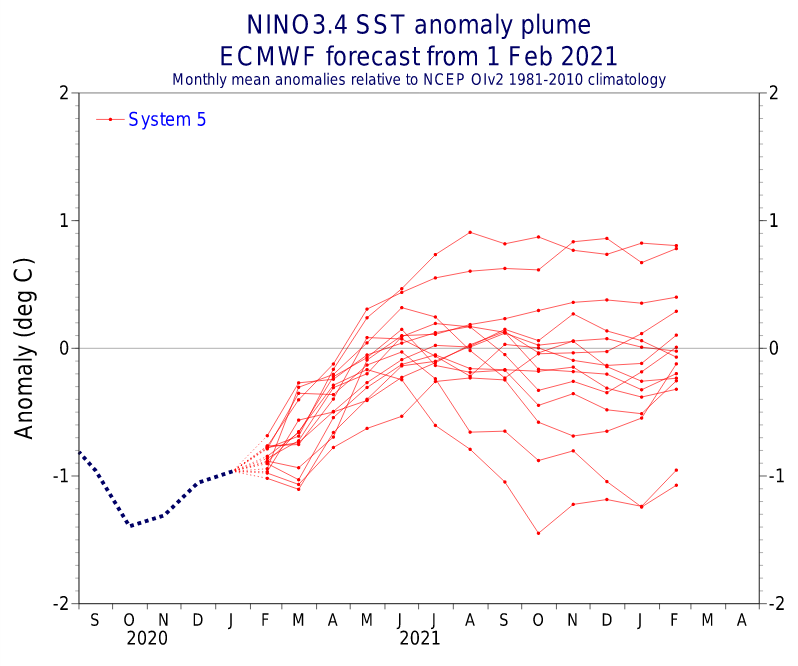
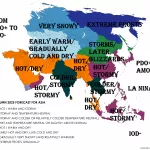
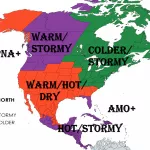
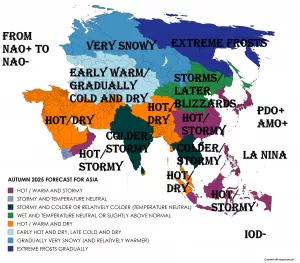
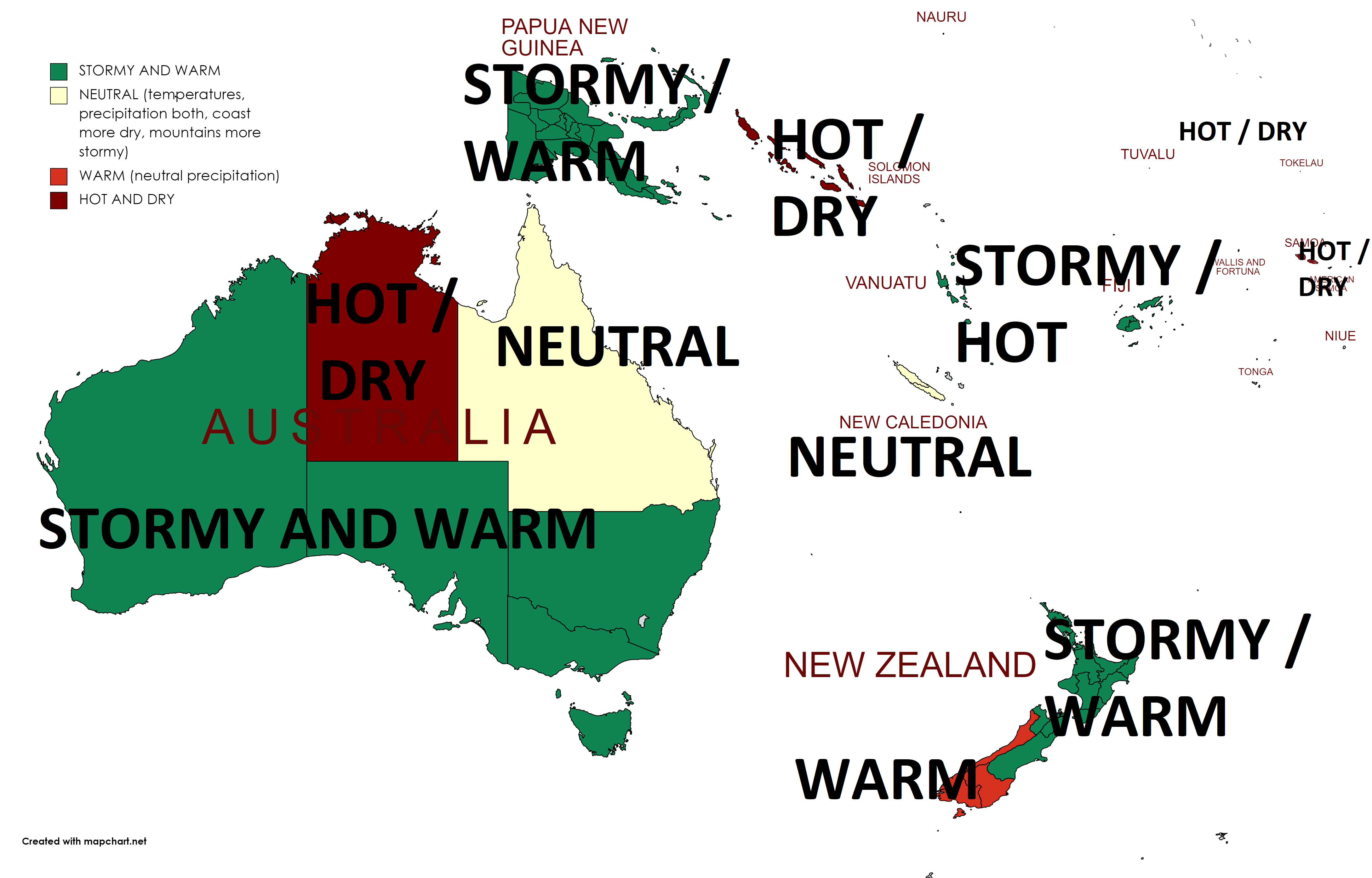
Similar pattern such as in Summer 2020/2021 and Autumn 2021 /https://mkweather.com/autumn-2021-forecast-for-australia-2021/; https://mkweather.com/summer-2020-2021-forecast-for-australia-new-zealand-and-oceania// is prepared for the continent again, with weakening La nina and stormy conditions in western and southern half of Australia /https://mkweather.com/the-coldest-earth-for-7-years-strong-impact-of-la-nina-is-here///.
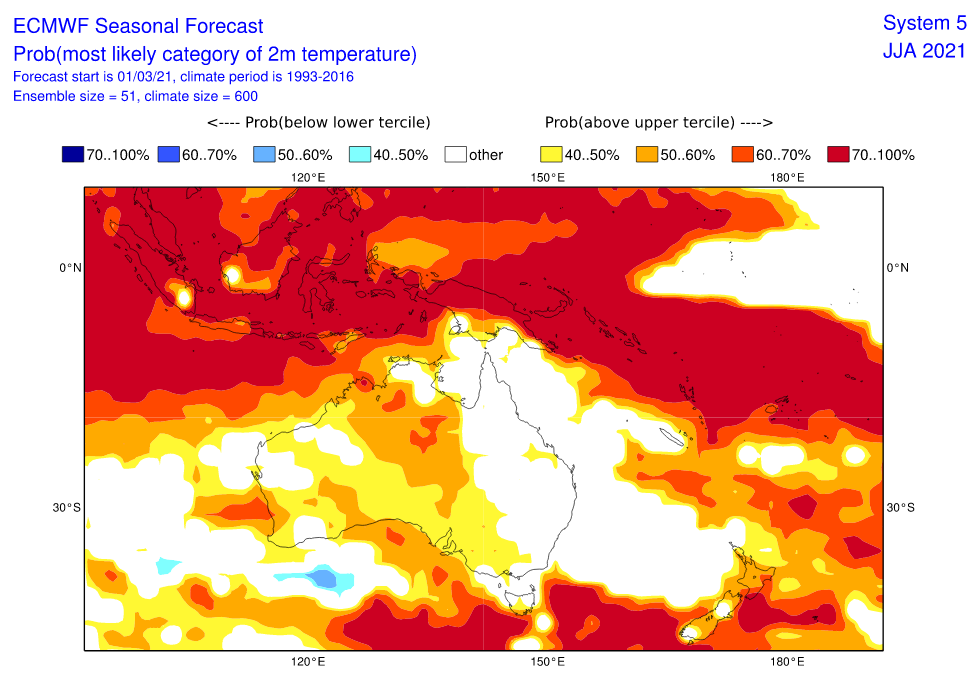
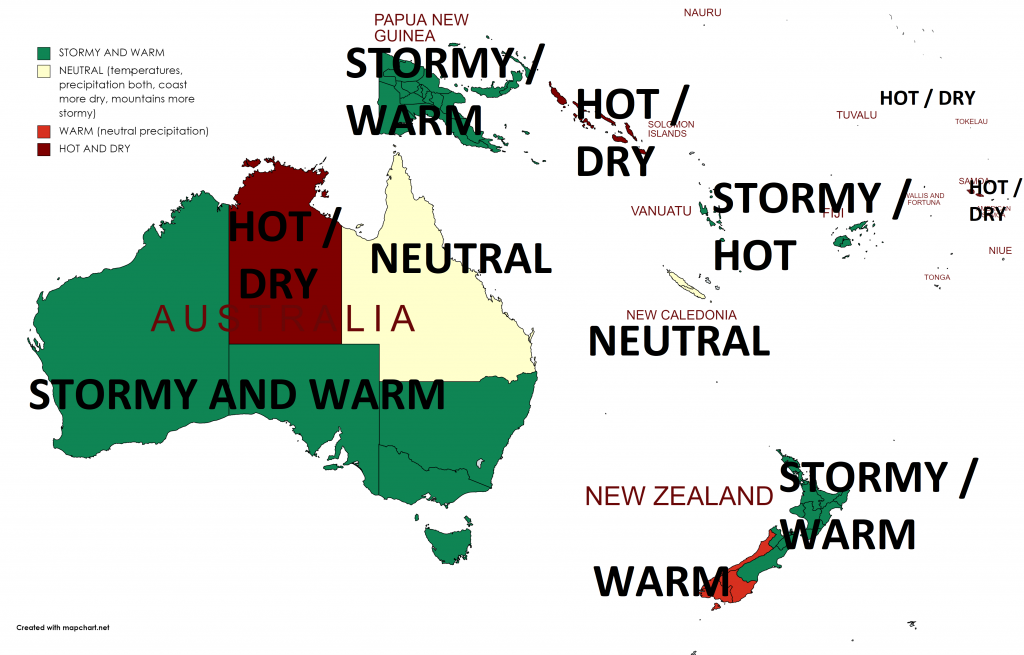
Only Northern Territory appears thanks to extremely war continental air masses and season of drought very hot and dry.
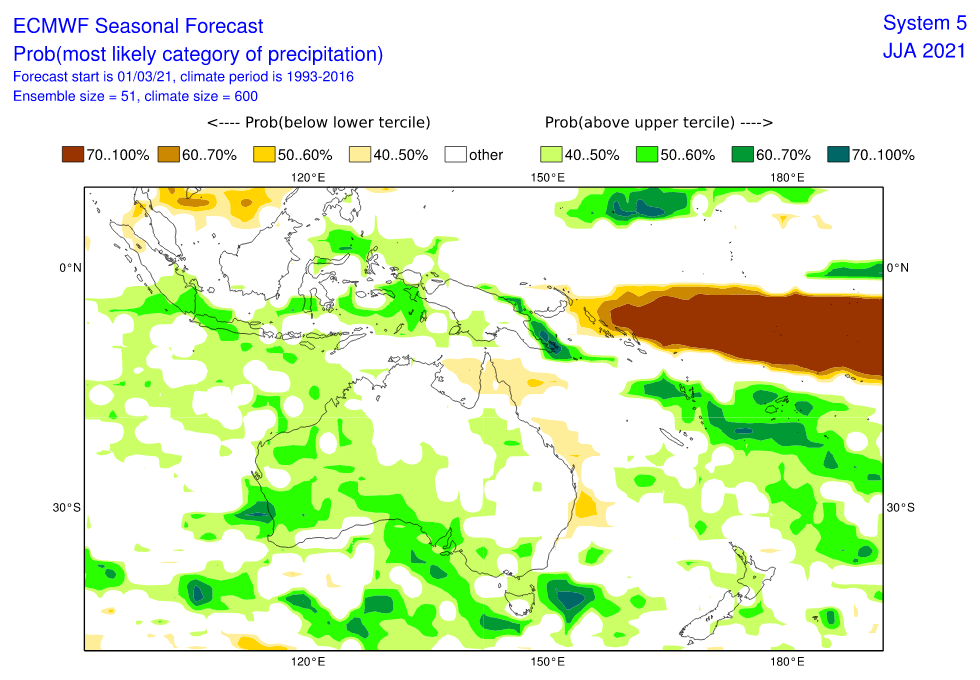
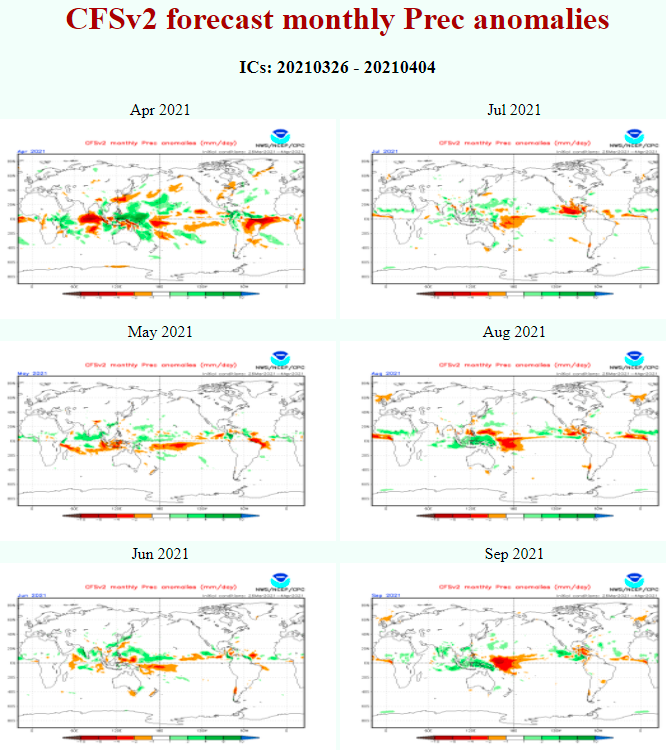
Queensland appears neutral, but with above average precipitation in mountains and below average precipitation along the coast.
Stormy and warm, in northern islands hot weather, is expected in many parts of New Zealand, Papua – New Guinea, Fiji or Vanuatu, while La nina brings hot and dry weather to Solomon Islands, Tuvalu or Samoa.
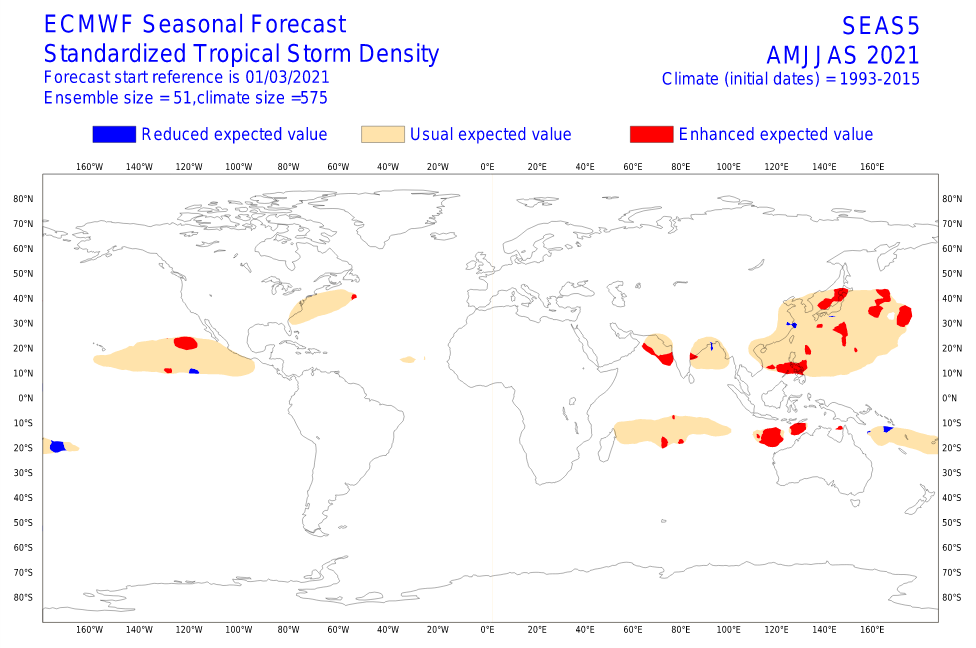
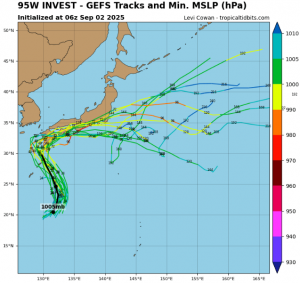
Above average activity of tropical cyclones is during summer season (AMJJAS) forecasted northwestward from Australia – some cyclones should hit coastal areas, too.
Below average activity of cyclones is expected in southern Solomon Islands region and therefore partly in Queensland (neutral trends and dry coast).
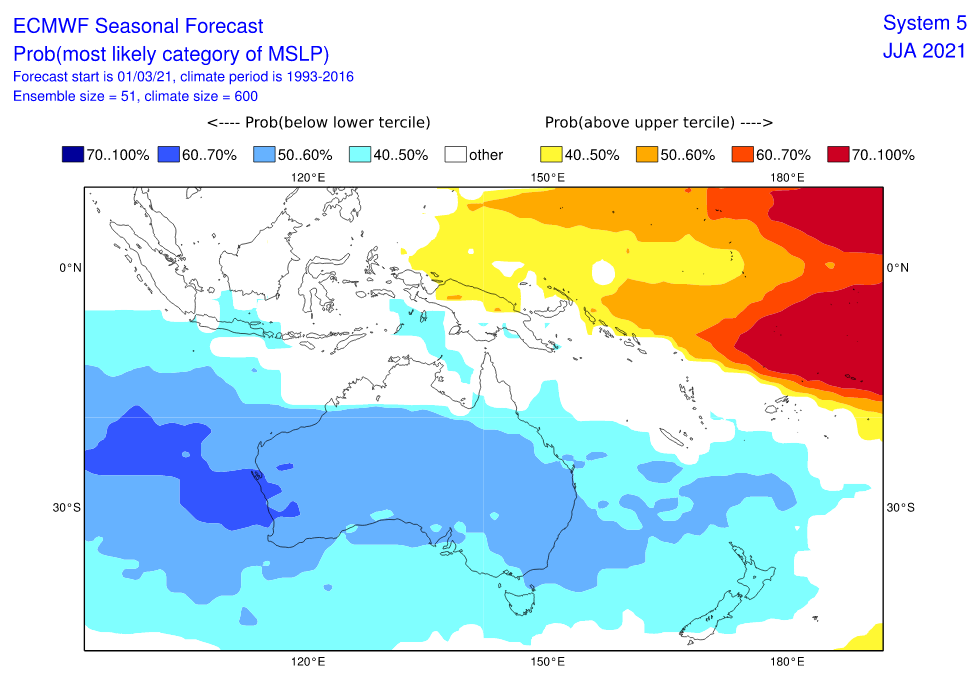
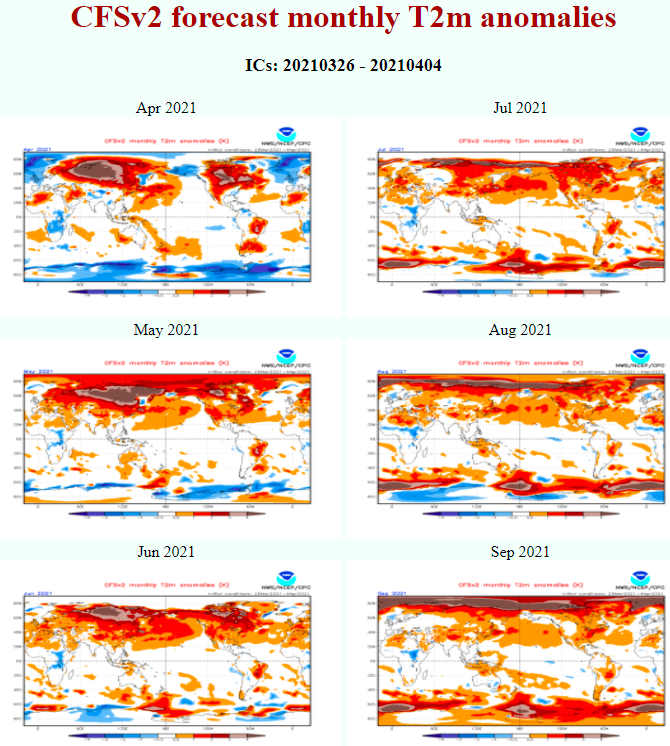
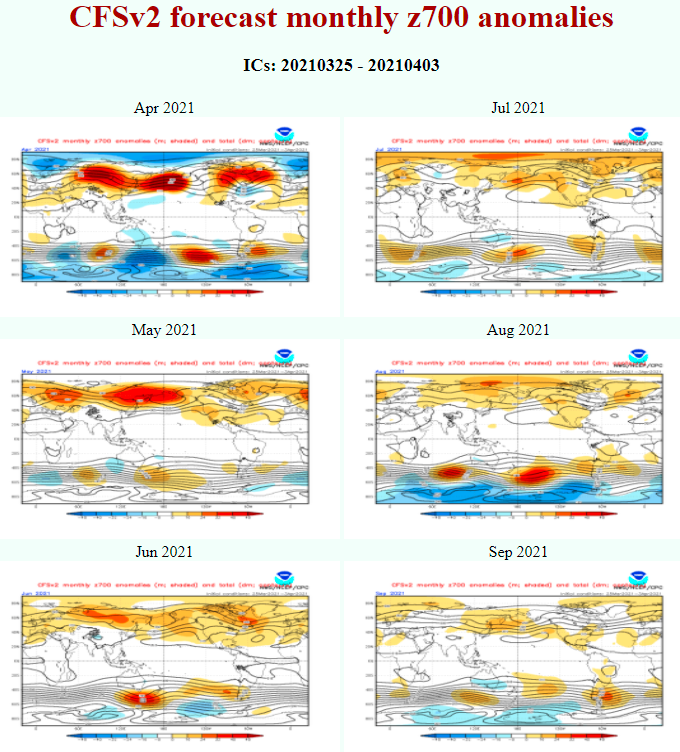
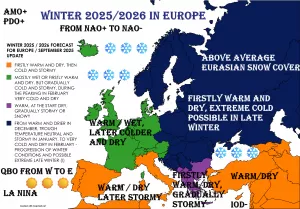
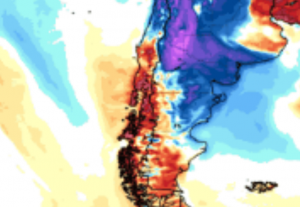
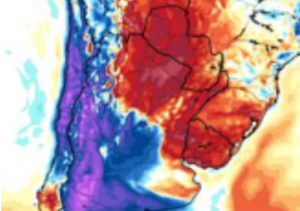
Last runs of CFSv2 model expect above average geopotential southward from Australia and New Zealand in June 2021, but low geopotential above densely populated regions in S/SE Australia in July 2021.
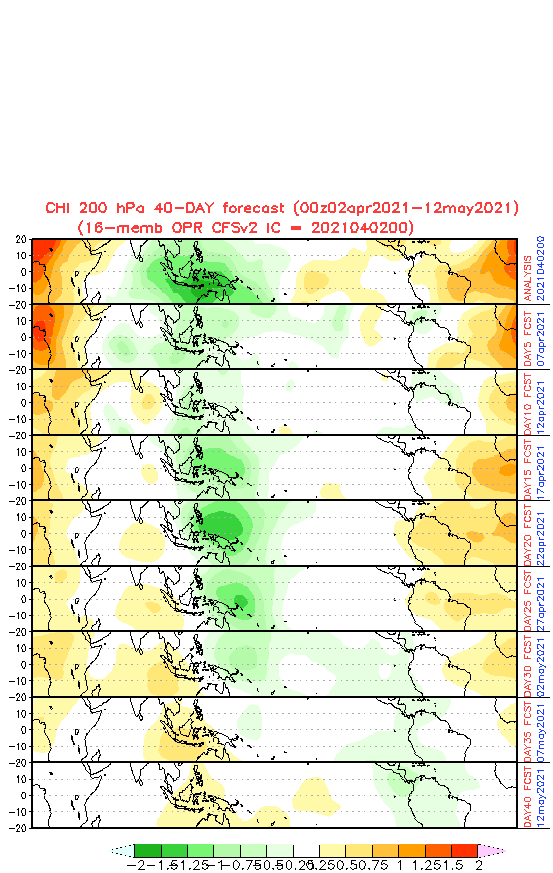
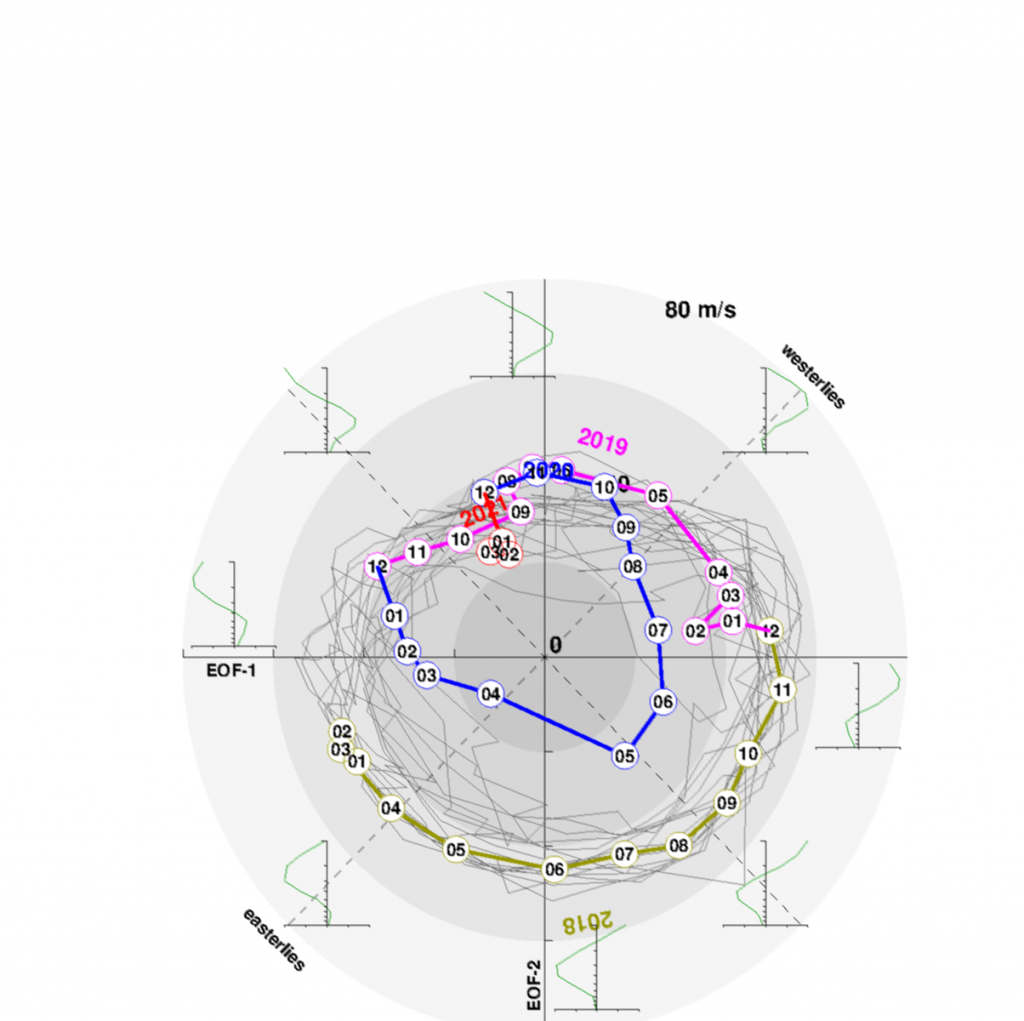
MJO is forecasted to shift into dry phase around the half of May 2021 after long wet phase. If dry phase will persist into June, activity of cyclones should be in early Summer weak.
Winter in Antarctica should be very cold, after experiences from Summer 2020/2021 and Autumn 2021, when coldwaves were bringing almost monthly historical continental records /https://mkweather.com/first-700c-in-antarctica-of-the-season-continent-is-still-extremely-cold/; https://mkweather.com/east-antarctica-not-warming-past-4-decadescooling-trend/; https://mkweather.com/summer-in-antarctica-603c-only-42c-warmer-as-all-time-monthly-continental-record-extreme-cold-2021/; https://mkweather.com/antarctica-set-to-coldest-january-since-1978-southern-hemisphere-hasnt-been-so-cold-almost-10-years//.
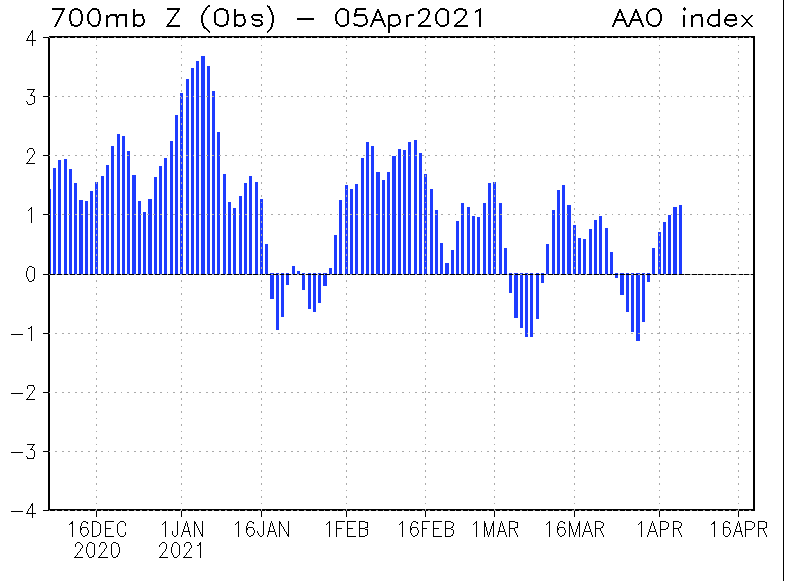
Dominating AAO+ phase since Summer 2020-2021 should mean stronger zonal circulation in parts of Southern Ocean and lot of winterstorms for researchers on the coast of Antarctica.
Infographics – Sources:
CFSv2 Seasonal Climate Forecasts (noaa.gov)
CPC – Climate Weather Linkage: Madden – Julian Oscillation (noaa.gov)
The Quasi-biennial Oscillation (QBO) (nasa.gov)